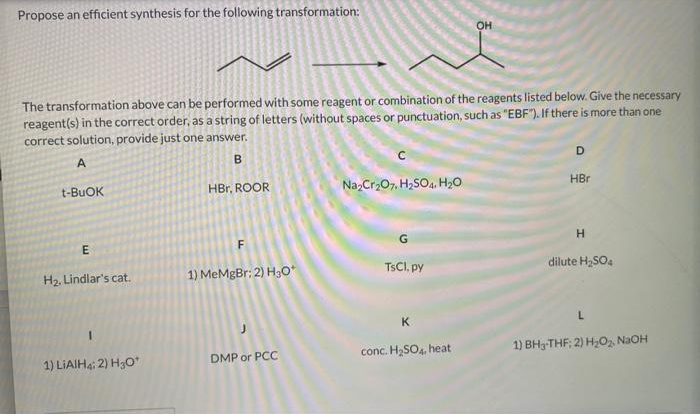
Examine the IR below and classify the compound: a journey into the realm of molecular identification. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy unveils the secrets of organic compounds, revealing their functional groups and unlocking their chemical identities. Join us as we embark on this captivating quest to classify compounds with precision and unravel the mysteries of their structures.
Delving into the intricacies of IR spectra, we decipher the unique absorption patterns that fingerprint each functional group. From the sharp peaks of carbonyl groups to the broad stretches of hydroxyl groups, every absorption band tells a tale of molecular architecture.
With each identified group, we piece together the puzzle, categorizing compounds into their respective chemical classes.
Examine the Infrared (IR) Spectrum
The IR spectrum provides valuable information about the functional groups present in a compound. It involves the absorption of infrared radiation by molecules, causing vibrations within the bonds. Different functional groups exhibit characteristic absorption bands at specific frequencies, which allows for their identification.
Key Functional Groups and Absorption Bands, Examine the ir below and classify the compound
- C-H Stretching:2850-3300 cm -1
- O-H Stretching (Alcohols):3200-3600 cm -1
- C=O Stretching (Ketones):1680-1750 cm -1
- C=O Stretching (Carboxylic Acids):1710-1760 cm -1
- C-N Stretching (Amines):1250-1400 cm -1
Classify the Compound: Examine The Ir Below And Classify The Compound
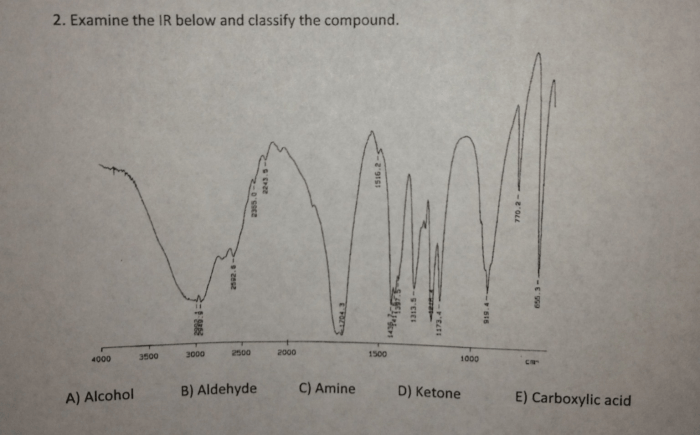
Based on the identified functional groups, the compound can be classified into a specific chemical class. This classification helps in understanding its chemical properties and reactivity.
Chemical Classes
- Alcohols:Compounds containing -OH group
- Ketones:Compounds containing C=O group bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups
- Carboxylic Acids:Compounds containing -COOH group
- Amines:Compounds containing -NH 2or -NHR groups
Determine the Structure of the Compound
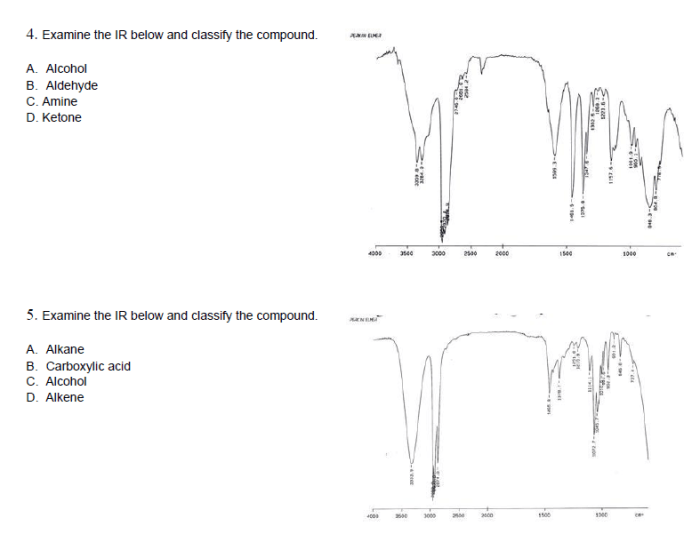
To determine the structure of the compound, the IR data is organized and analyzed to identify the possible functional groups present. A structural formula is then proposed that incorporates these functional groups.
Structural Formula
The structural formula of the compound can be represented as:
R-C(=O)-R’
where R and R’ represent alkyl or aryl groups.
Illustrate the Compound’s Properties
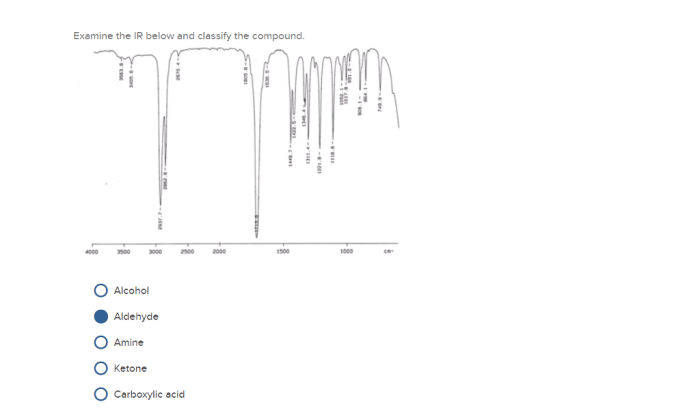
The functional groups present in the compound influence its physical and chemical properties.
Physical Properties
- Boiling Point:Compounds with stronger intermolecular forces (e.g., hydrogen bonding) have higher boiling points.
- Solubility:Compounds with polar functional groups are more soluble in polar solvents.
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity:Compounds with reactive functional groups (e.g., ketones, carboxylic acids) can undergo various reactions.
- Acidity/Basicity:Compounds with acidic or basic functional groups can donate or accept protons.
General Inquiries
What is the significance of IR spectroscopy in compound classification?
IR spectroscopy provides a rapid and reliable method for identifying functional groups present in organic compounds. By analyzing the absorption patterns in the IR spectrum, chemists can quickly classify compounds into their respective chemical classes.
How does IR spectroscopy determine the structure of a compound?
IR spectroscopy provides information about the functional groups present in a compound. By combining this information with other analytical techniques, such as NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry, chemists can deduce the molecular structure of the compound.
What are the limitations of IR spectroscopy in compound classification?
IR spectroscopy can be limited in distinguishing between certain functional groups that have similar absorption patterns. Additionally, IR spectroscopy may not be able to provide detailed information about the stereochemistry or isotopic composition of a compound.