Lesson 4 making circuit calculations for basic systems – Lesson 4: Making Circuit Calculations for Basic Systems delves into the fundamental concepts of electrical circuits, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding voltage, current, and resistance. This lesson empowers learners with the knowledge and skills necessary to analyze and design simple circuits, laying the foundation for further exploration in electrical engineering.
Through a combination of theoretical explanations, practical examples, and real-world applications, this lesson equips readers with the ability to calculate circuit parameters, troubleshoot electrical systems, and design circuits to meet specific requirements. Whether you’re a student, hobbyist, or professional, this lesson offers valuable insights into the fascinating world of electrical circuits.
Basic Circuit Calculations: Lesson 4 Making Circuit Calculations For Basic Systems
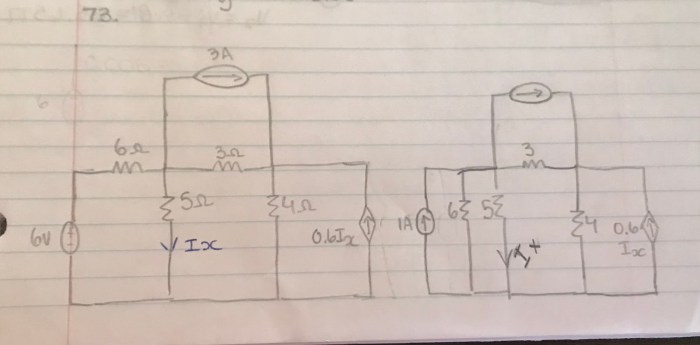
Circuit calculations form the foundation of electrical engineering and troubleshooting. They enable engineers and technicians to design, analyze, and maintain electrical systems efficiently and safely. This lesson provides an overview of basic circuit calculations, covering fundamental concepts, series and parallel circuits, circuit analysis techniques, and practical applications.
Understanding the principles of voltage, current, and resistance is crucial for circuit calculations. Voltage represents the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit, while current measures the flow of electric charge. Resistance quantifies the opposition to current flow.
These three quantities are related by Ohm’s Law, which states that the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it.
Series Circuits, Lesson 4 making circuit calculations for basic systems
- In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end, forming a single path for current flow.
- The total resistance of a series circuit is the sum of the individual resistances.
- The voltage across each component is inversely proportional to its resistance, and the current through all components is the same.
Parallel Circuits
- In a parallel circuit, components are connected side-by-side, providing multiple paths for current flow.
- The total resistance of a parallel circuit is less than the smallest individual resistance.
- The voltage across each component is the same, and the current through each component is inversely proportional to its resistance.
Circuit Analysis Techniques
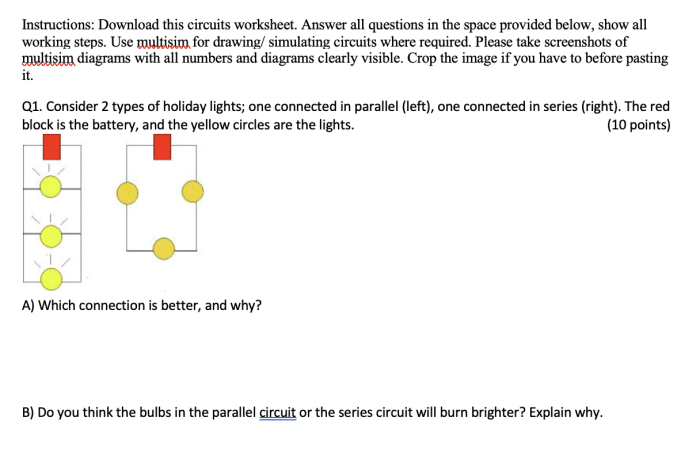
Circuit analysis techniques provide systematic methods for simplifying and solving complex circuits. Ohm’s Law is a fundamental tool, allowing engineers to calculate voltage, current, and resistance in various circuit configurations.
Voltage Dividers
Voltage dividers are circuits that distribute voltage across multiple resistors. They are used to create specific voltage levels or to measure voltage.
Current Dividers
Current dividers are circuits that distribute current through multiple resistors. They are used to control current flow or to create specific current levels.
Equivalent Resistance
Equivalent resistance is a technique for simplifying complex circuits by replacing multiple resistors with a single equivalent resistor. This simplifies circuit analysis and reduces the number of calculations required.
Applications of Circuit Calculations
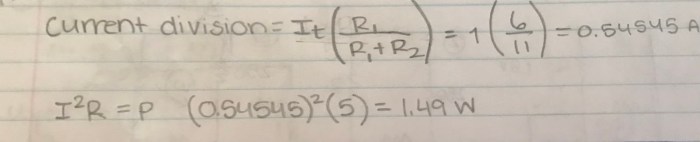
Circuit calculations have numerous practical applications in electrical systems. Engineers use them to design circuits that meet specific requirements, such as voltage regulation, current limiting, and power dissipation.
- Designing circuits to power electronic devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and industrial equipment.
- Calculating the current and voltage requirements of electrical motors and generators.
- Troubleshooting electrical systems to identify and repair faults.
Circuit calculations are essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems, from simple household circuits to complex industrial control systems.
FAQ Insights
What is the difference between series and parallel circuits?
In a series circuit, components are connected one after another, while in a parallel circuit, components are connected side by side. This difference affects the flow of current and the distribution of voltage in the circuit.
How can I calculate the total resistance of a series circuit?
To calculate the total resistance of a series circuit, simply add the resistances of all the individual components.
What is Ohm’s Law and how is it used in circuit analysis?
Ohm’s Law states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it. This law is used to calculate voltage, current, or resistance in a circuit when two of the three quantities are known.