Match the epithelial tissue with the correct description is a topic that delves into the fascinating world of epithelial tissues, the guardians of our bodies. This comprehensive guide unveils the diverse types, functions, locations, adaptations, regeneration, diseases, and ongoing research surrounding these remarkable tissues.
Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey that unravels the intricacies of epithelial tissues, their crucial roles, and their significance in human health.
Epithelial tissues, the gatekeepers of our bodies, line the surfaces of organs and cavities, forming a protective barrier against external threats. They exhibit a remarkable diversity, each type meticulously adapted to its specific location and function. Understanding the characteristics that distinguish each type is essential for comprehending their roles in maintaining homeostasis and protecting against disease.
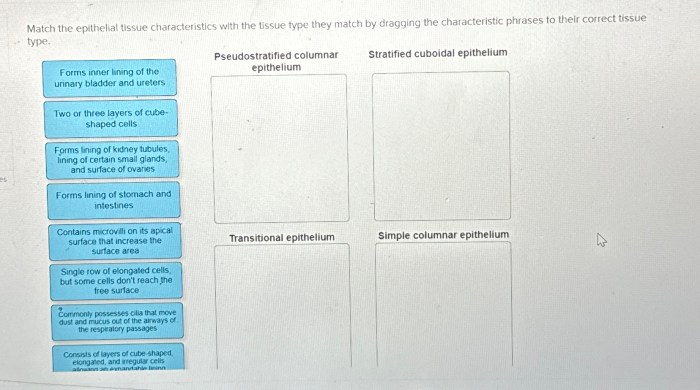
Epithelial Tissue Classification: Match The Epithelial Tissue With The Correct Description

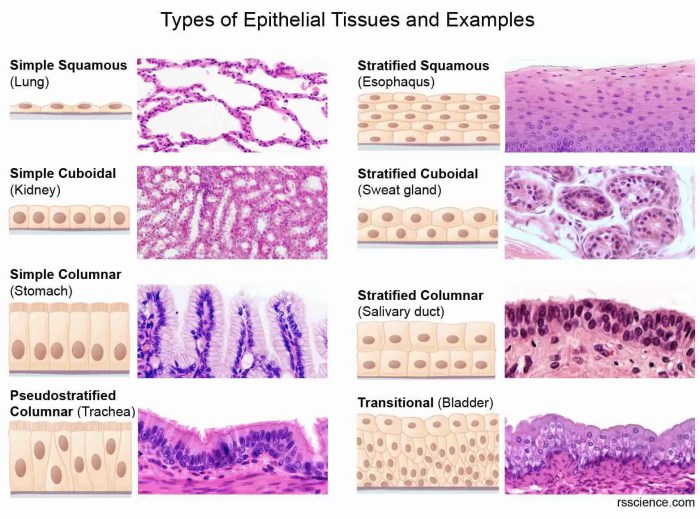
Epithelial tissues are classified based on their shape, arrangement, and number of cell layers. The main types of epithelial tissues include:
- Simple epithelium:Consists of a single layer of cells. It can be further classified into:
- Squamous epithelium: Flat, scale-like cells
- Cuboidal epithelium: Cube-shaped cells
- Columnar epithelium: Tall, column-shaped cells
- Stratified epithelium:Consists of multiple layers of cells. It can be further classified into:
- Stratified squamous epithelium: Multiple layers of squamous cells
- Stratified cuboidal epithelium: Multiple layers of cuboidal cells
- Stratified columnar epithelium: Multiple layers of columnar cells
- Pseudostratified epithelium:Appears to be stratified, but all cells are attached to the basement membrane. It can be further classified into:
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium: Tall, column-shaped cells with varying heights
- Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium: Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia on the surface
- Transitional epithelium:Can change shape depending on the degree of stretching. Found in the urinary bladder and urethra
Clarifying Questions
What are the key characteristics of epithelial tissues?
Epithelial tissues are characterized by their close packing, forming continuous sheets or layers, and their polarity, with distinct apical and basal surfaces.
How do epithelial tissues contribute to homeostasis?
Epithelial tissues play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis by regulating the movement of substances across their surfaces, protecting against pathogens, and facilitating gas exchange.
What are some common diseases that affect epithelial tissues?
Epithelial tissues are susceptible to a variety of diseases, including cancer, infections, and inflammatory conditions.